Heat pumps | The ultimate guide
To prevent climate change and secure its energy supplies, the UK needs to reduce its dependence on natural gas. A recent government report found that 90% of all homes continue to use boilers that burn natural gas for central heating. To reduce gas consumption, the government is encouraging replacing traditional boilers with heat pumps.
This guide looks at what they are, how they work, and how your business can benefit from switching to a heat pump.
What is a heat pump?
A heat pump is a device that captures heat from outside your property and moves it to the interior to heat your rooms. Unlike a gas boiler, a heat pump uses electricity and is significantly more efficient than a conventional central heating system.
A heat pump works by capturing the heat already present around your property, reducing the energy and cost you need to keep your property warm.
In early 2022, the wholesale cost of gas soared. Warming properties with traditional central heating systems using boilers are costing businesses significantly more. Compare business gas with AquaSwitch.
How does a heat pump work?
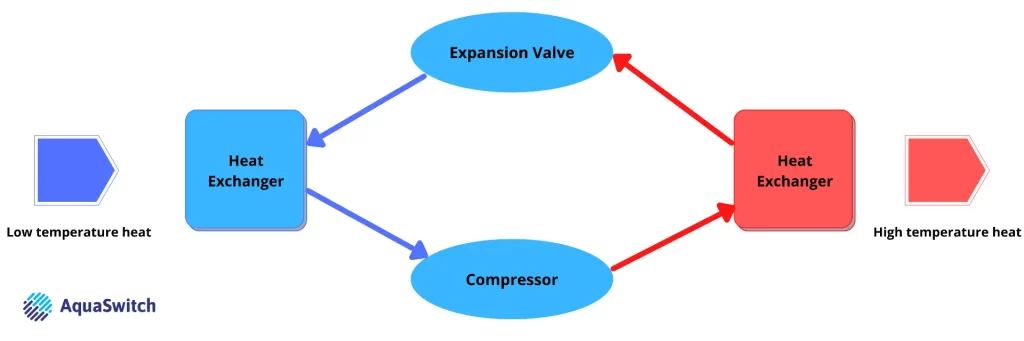
A heat pump works by absorbing heat externally from the air, water, and ground, then transferring it to your property’s existing radiator system or underfloor heating.
A heat pump works in a similar way to your fridge, using pressure changes in gas, known as a refrigerant, to increase or lower the temperature in different places.
Outside your building, the refrigerant is compressed by the heat pump using electricity, increasing the pressure and temperature. The heat energy is transferred into your property using a heat exchanger. The heat exchanger takes the heat from the refrigerant and uses it to warm radiators inside your property.
Once complete, the remaining refrigerant expands and cools down. The heat pump is now cold enough to absorb more heat from outside and begin the process again.
What are the different types of heat pumps?
Let’s dive into the two main types of heat pumps:
Air source heat pump
An air source heat pump is a system that absorbs heat energy from the air outside. It works by the outside air being blown over multiple tubes filled with refrigerant.
A compressor causes the refrigerant to rise in temperature. The warm refrigerant passes through a heat exchanger into your property, where it warms water in your central heating system. The refrigerant then condenses back into a liquid and is cooled to begin the cycle again.
Ground source heat pump
A ground source heat pump uses heat from the ground outside your business premises to extract heat..
A ground source heat pump uses a liquid called a “Thermal transfer fluid (TFF)”, which is a mix of antifreeze and water – that flows through an underground pipe loop. The pipe loop will either be a coiled pipe buried in trenches or a longer loop pipe inserted into a borehole with a diameter of over 180mm.
The heat from the ground will be absorbed into the fluid that passes through the heat exchanger and into the pump for this to work. It raises the temperature of the fluid and transfers the heat into the property.
How efficient is a heat pump?
A question commonly asked, “How efficient is a heat pump?” Firstly, it depends on the type of heat pump used.
How efficient is a ground source heat pump?
A ground source heat pump is very energy efficient. For every unit of electricity it uses, four units of heat are transferred. This means that a ground source heat pump will be 400% more efficient than its electricity usage.
At this efficiency level, you will see around 70-75% fewer carbon emissions than that of a gas boiler. And if your business is on a renewable business energy tariff, your carbon emissions will be zero.
How efficient is an air source heat pump?
An air-source pump is not as efficient as a ground-source pump, but it is still around 300% efficient. For every unit of energy it uses, it outputs three units of heat energy into the premises.
Is a heat pump classed as renewable?
Unlike traditional central heating systems, heat pumps do not directly burn natural gas. Instead, a heat pump uses electricity. If your business uses a green business energy supplier, then your electricity will be renewable, as well as the heating of your property.
Renewable sources of electricity are generated from tidal, solar, wind, or nuclear power.
How much does a heat pump cost?
Heat pumps are a great way to reduce your business’s carbon footprint, but how much do they cost? Air source heat pumps will cost you between £3,000 and £18,000, depending on the pump you choose.
If you’re a homeowner, it’s worth looking into the government’s £5,000 scheme to replace household boilers with heat pumps.
The short-term costs of installing a heat pump are offset by a reduction in energy costs due to the improved efficiency of the heat pump system. Businesses pay for electricity and gas supplies at an agreed unit rate per kWh of energy consumed. By installing a heat pump, you’ll be using significantly less energy and will save money each month. Compare business energy with AquaSwitch today.
In some regions of the UK, companies can apply for a business energy grant to reduce the cost of installing a heat pump.
Do I need permission to install a heat pump?
No, since 2011 in England, every type of heat pump is considered a “permitted development”. This means no planning permission is needed to implement and install.
This was made legal at the end of 2011 as the government looked to push for accessibility to renewable heat sources.
Advantages vs disadvantages of heat pumps
Here, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using a heat pump over a regular gas boiler.
Advantages of a heat pump
Installing a heat pump can significantly reduce your business’s carbon emissions, but there are other benefits too:
- Less maintenance in comparison to gas boilers.
- Safer than gas boilers.
- Lower running costs in the long term, the initial cost is offset by huge long-term savings.
- Have a longer life span compared to gas boilers.
- No need to pay business gas rates.
Using a heat pump allows your business to avoid purchasing expensive natural gas from a business gas supplier.
Disadvantages of a heat pump
Here are a few disadvantages of using a heat pump. From being expensive and complex to install, we delve deeper into the disadvantages of a heat pump:
- More expensive than a gas boiler initially.
- Installation can be complex.
- Requires significant work to install correctly.
- If using non-renewable electricity supplies, the renewable/sustainability factor is questionable.
Overall, as a business, you need to weigh the pros and cons and look at the long term. Does this suit your business? Is it practical? And does it fit within your sustainability plans for the future?
UK heat pump government scheme (BUS) – what is it? And how do I apply?
The heat pump scheme (Boiler Upgrade Scheme) is part of a government scheme that encourages property owners to install low-carbon heating systems such as heat pumps. It will run from 2022 to 2025.
Eligibility:
- All domestic properties.
- and small non-domestic properties in England and Wales.
Are you looking to switch to a sustainable energy source?
Use the AquaSwitch to compare business electricity prices and switch business energy suppliers.
You can compare 100% renewable tariffs as well as combined tariffs by using our simple postcode finder to begin the comparison.
Heat pumps – FAQs
We answer your frequently asked question on heat pumps.
Do heat pumps work with radiators?
Yes, they do. Heat pumps can be used to heat properties either through radiators, underfloor heating, or both combined. Heat pumps work well with radiators and produce enough heat to warm your premises.
Are heat pumps noisy?
Not as noisy as a gas boiler. It makes some noise when heating the water or air, but generally no more than a fossil fuel-based gas boiler.
A ground source heat pump is generally quieter at around 40 decibels, whereas an air source heat pump can reach 40-60 decibels, depending on the installation and manufacturer.