Understanding Half Hourly Meters
Since 2017, British businesses with high electricity demand are required to have a half-hourly energy meter that records their electricity consumption on a real-time basis.
There are over 100,000 such half-hourly meters in operation in Britain, and these are located in businesses like factories, large offices or department stores that use a lot of energy.
This guide provides a comprehensive look into half-hourly business energy meters. We will explain what they are, how they work, and their cost implications.
💡Half-hourly meters are mandatory for businesses whose electricity demand peaks at 100kW or more during any 30-minute period – approximately equivalent to fast charging 10 EV vehicles or boiling 35 kettles simultaneously.
Key takeaways:
- Businesses with a supply number (MPAN) starting “00” have a half-hourly meter that automatically sends meter readings every 30 minutes to their electricity supplier.
- Businesses with half-hourly meters have access to energy analytics tools from their suppliers, enabling effective monitoring and management of energy consumption.
- Businesses with lower electricity usage can upgrade to smart energy meters, which offer direct communication with business energy monitors.
How do half-hourly meters work?
The technology in a half-hourly meter is surprisingly basic. Like all electricity meters, a half-hourly meter measures the number of kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy that is consumed at a commercial property.
As each kWh of electricity flows through the meter, the digital dial on the front will increase by one unit. The meter measures the amount of electricity consumed as the difference between the meter readings over time, for example:
01 January 2024 – Meter reading – 0054224
31 January 2024 – Meter reading – 0773254
Electricity used in January 2024: 719,030 kWh
What makes a half-hourly meter unique is that the meter will automatically record meter readings every half-hour continuously. The meter uses a mobile signal or fixed phone line to transmit this data (via a data communications company) to your business energy supplier.
The benefits and drawbacks of half-hourly meters
In this section, we’ll delve into the key benefits and drawbacks of half-hourly metering for business owners.
What are the benefits of half-hourly metering?
- Detailed energy consumption data: half-hourly energy metering provides businesses with accurate and detailed data on their energy usage patterns. This data can be used to identify areas of high energy usage and to measure the impact of energy efficiency measures taken in a business energy audit. Reducing energy consumption will not only cut electricity costs but also decrease their associated carbon footprint.
- Improved energy management: Using accurate and detailed data on energy consumption, businesses can better manage the timing of their energy usage. By actively controlling the timing of high-consumption activities, such as EV charging, businesses can optimise their energy costs by taking advantage of lower off-peak rates and even earn money through the demand flexibility service.
- Accurate business electricity bills: Half-hourly metering allows suppliers to issue business electricity bills based on actual usage rather than manual meter readings or estimations. This approach eliminates estimated billing and overcharging, providing companies with certainty over their electricity expenses.
What are the issues with half-hourly metering?
- Installation and maintenance costs – The installation and maintenance costs associated with half-hourly energy metering can be significant. Additionally, half-hourly meters require regular maintenance to ensure accurate readings, which can result in higher business energy standing charges.
- Data management – The vast amount of data generated by half-hourly energy meters can be daunting, particularly for businesses that lack the necessary resources or expertise to effectively manage and analyse this data. Without proper data analysis, businesses may miss opportunities to identify inefficiencies and implement energy-saving measures.
- Dependency on energy suppliers – Half-hourly energy metering requires businesses to rely on their energy suppliers to provide accurate and timely data on their energy consumption. This dependency makes the process of switching business energy suppliers more complex.
- Complexity – The introduction of half-hourly metering for electricity results in a bewildering array of additional charges associated with business energy supplies. This increased complexity imposes an administrative burden on business operators and owners.
Should I upgrade to a half-hourly meter?
The P272 regulation gives businesses that have a maximum demand exceeding 70kW the option of upgrading to a half-hourly meter (while businesses with a maximum demand over 100kW half-hourly meters are legally obligated).
We recommend that businesses that are not required to have half-hourly meters instead consider a smart energy meter. Smart meters are modern devices capable of taking automatic readings at intervals of your choosing. They provide the added benefit of allowing you to access this data directly using a business energy monitor rather than relying solely on data from your supplier. This approach offers more flexibility and control over your energy data management.
Half-hourly meter data
A half-hourly energy meter sends your consumption data to your supplier every 30 minutes. The best business energy suppliers provide a data analysis portal for their large business energy customers, allowing you to access your half-hourly energy consumption data.
Here are links to the energy platform operated by the biggest business energy suppliers:
- SSE – SSE clarity
- British Gas – Energy360
- EDF – Energy View
- E.ON – E.ON Optimum
- Drax – Energy Assistant
- Scottish Power – Dataserve
These portals provide a straightforward way to access and analyse your business’s electricity consumption. They compile the half-hourly meter data into interactive reports, enabling you to compare daily consumption across your properties. Such reports are invaluable for quickly identifying and addressing inefficiencies in your electricity usage.
Costs associated with half-hourly meters
The business electricity rates for companies with half-hourly meters are often more complex than the simpler, fixed business energy tariffs typically paid by smaller companies. Below, we provide a summary of the various cost implications that come with having a half-hourly meter.
Maximum demand charges
A maximum demand charge is a monthly amount paid to your local distribution network operator to guarantee the availability of a specific amount of power capacity at your property (Agreed Power Capacity). The maximum demand capacity is charged as a fixed daily charge by your business energy supplier.
If your business exceeds the maximum demand capacity in any half-hour period, your supplier may charge an excess demand charge.
For a more detailed understanding, check out our full guide to maximum demand charges.
Off-peak business electricity rates
Using the real-time consumption data, half-hourly business electricity tariffs will typically define different rates per kWh of electricity supplied at different times of the day. With these tariffs, your business will benefit from the cheaper cost of electricity at night time by paying lower electricity costs outside of peak hours.
Meter operator and data collection charges
Businesses with a half-hourly meter will need to pay a meter operator charge to the company that installed your meter. These annual charges are typically in the range of £300 to £600, paid for the supply, maintenance and communication costs associated with your half-hourly meter.
Usually, businesses have meter operator agreements that are separate from their business electricity tariffs. As a result, these charges are often billed separately each month.
Half-hourly meters for business – FAQs
Our experts answer the most commonly asked questions surrounding half-hourly energy meters.
P272 regulation on half-hourly meters
P272 is a regulation that came into effect in November 2015, requiring that businesses with a peak load electricity usage exceeding 100kW have their energy usage recorded every half an hour.
The regulation was the first step towards a smart grid where distribution network operators started to measure accurately how large users consume electricity to improve grid management.
Since then, the government and regulators have also rolled out automatic meter readings for small businesses and domestic users through the smart meter universal roll-out.
Source: Ofgem – Moving to half-hourly energy reads
How do I know if my business has a half-hourly meter?
You can tell if your business has a half-hourly meter by checking the number next to the S on your bill (also known as the Meter Point Administration Number or MPAN). If the number starts with 00, then your business is equipped with a half-hourly meter.
Here’s what to look out for:
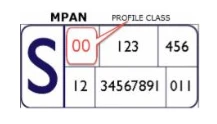
Credit: https://thesmartmeter.co.uk/
What is a Half Hourly Meter Operator (MOP)?
A Half Hourly Meter Operator (MOP) is a company responsible for installing and maintaining half-hourly electricity meters. MOPs are licenced by the UK regulator, Ofgem, and are responsible for ensuring that the half-hourly meters are installed correctly and accurately record their customers’ electricity consumption.
They are also responsible for communicating the meter readings to the energy supplier, who uses them to calculate the customer’s business energy bill.
MOPs work closely with business energy suppliers and customers to ensure the half-hourly meters are working correctly and any issues are resolved quickly.
They may also provide additional services such as data analysis, energy management and reporting to help customers understand and reduce their energy consumption.
What is a Data Collector (DC)?
A Data Collector (DC) is a company that collects meter readings from half-hourly electricity meters on behalf of energy suppliers in the UK.
Data Collectors are licenced by the UK regulator, Ofgem, and are responsible for collecting the meter readings from the half-hourly meters using a variety of methods. Once collected, the DCs send the meter readings to the energy supplier, who uses them to calculate the customer’s energy bill.
They work closely with energy suppliers and MOPs to resolve any issues with the meter readings quickly and efficiently. They may also provide additional services such as data analysis and reporting to help energy suppliers and customers understand and manage their energy consumption.
What is a Data Aggregator (DA)?
A Data Aggregator takes half-hourly meter data and validates it so it can be used for billing and settlement purposes in line with industry requirements.
In the half-hourly metering process, the DCs collect readings from the half-hourly meters and send them to the DA. The DA then processes the data, checks for accuracy and consistency, and presents it in a standardised format for energy suppliers to use in their billing and energy management systems.
DAs play a crucial role in the half-hourly metering process by helping energy suppliers manage large volumes of metering data from multiple sources. They also help to ensure that the data is accurate, timely and presented in a consistent format.
DAs may also provide additional services such as data analysis, forecasting and reporting to help energy suppliers and customers better understand and manage their energy consumption.
Compare business electricity tariffs
To compare the latest prices, use the AquaSwitch business energy comparison service and find the best business electricity prices today.
